|
An Article entitled ( Compton effect (Compton Scattering ))
Adding Date: 21/05/2022
Views: 445
Published by: Al-Mustaqbal College Administration
|
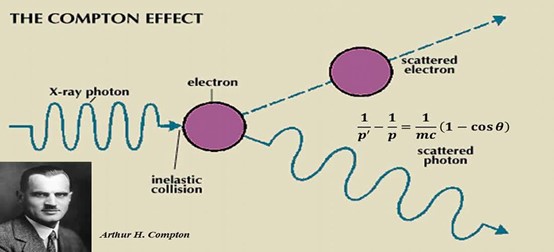
When a scattering of a high energy photon by a free charged particle (usually a loosely bound outer-shell electron in target material) results an increase in wavelength between scattered and initial photon, then it is called Compton Effect. It is also known as Compton Scattering. The Compton Effect is an incoherent and inelastic scattering of a photon by an elastic collision with electron in which both relativistic energy and momentum are conserved. Here both photon and electron treated as relativistic particles. Compton Effect results in both attenuation and also absorption of radiation. The difference between wavelengths of initial photon and scattered photon is known as Compton Shift. The Compton effect is based on treating light as consisting of particles of a given energy related to the frequency of the light wave. In this context, the particle of light is given the name “photon”. An energetic photon with energy of 0.1 MeV (million electron volts) or larger is also often referred to as a gamma ray. An MeV is an energy unit, equal to the kinetic energy an electron would gain by being accelerated through a voltage difference of 1 MV (106 volts). Photons whose energy is in the range of 0.1 to 100 keV are usually referred to as X-rays (1 keV = 10-3 of 1 MeV). The Compton Effect finds its application in radio-biology to:
treat cancer patients through radiation therapy. -
-Other applications of Compton Scattering include its use in the Compton Scatter Densitometer, which can be used to detect flaws or impurities in objects. Compton Scattering Imaging can measure the physical density of objects.
By Elaf Mehdi
|
|
|
|